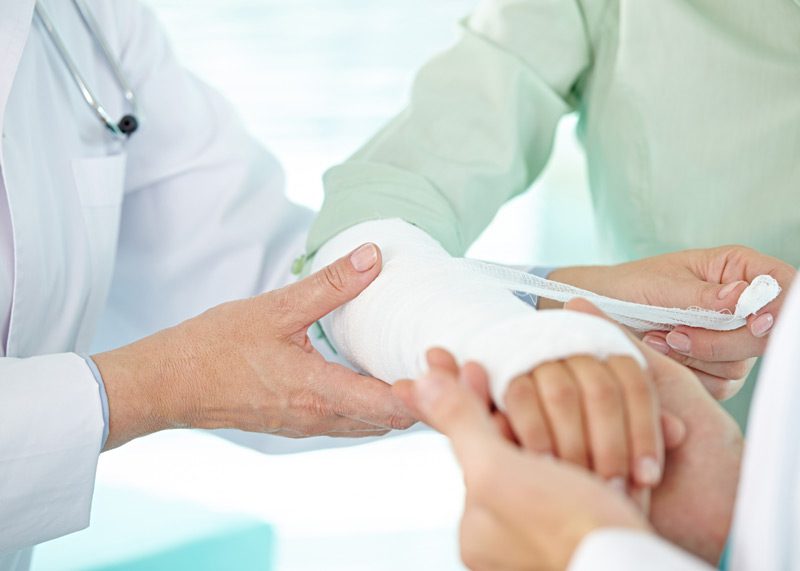
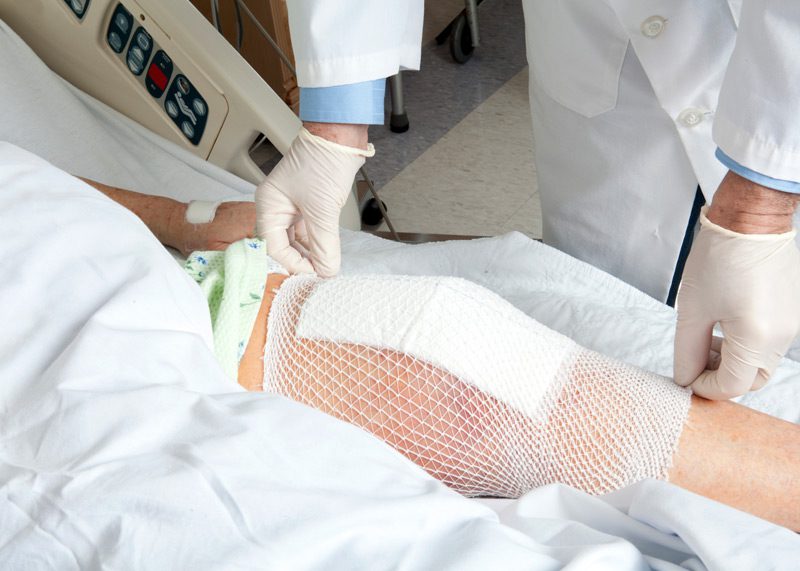

Active Plus Home Health Care, Inc. offers wound care and dressing changes to help patients fully recover from their injuries. A wound dressing supports healing and prevents future issues or complications. Depending on the type of wound, patients will need a specific type of dressing. However, all wound dressings are designed to:
- Stop bleeding
- Start clotting
- Absorb excess plasma, blood, and other fluid
- Remove dead skin cells
Symptoms of Wounds
Wounds can cause the following symptoms:
- Fever
- Malodorous pus drainage
- Heat
Complications of wounds include:
- Infection. This involves pus drainage, fever, foul odor, mild swelling, pain, and heat at the wound site.
- Scarring. Cells that grow following an injury contain fibrous tissue designed to heal the wound, but are likely to leave a scar.
- Inflammation. The wound can be hot, painful, swollen, red, and hard to move.
- Dysfunction. Severe wounds can damage a major organ, blood vessel, or nerve, increasing the risk of losing a limb or functionality.
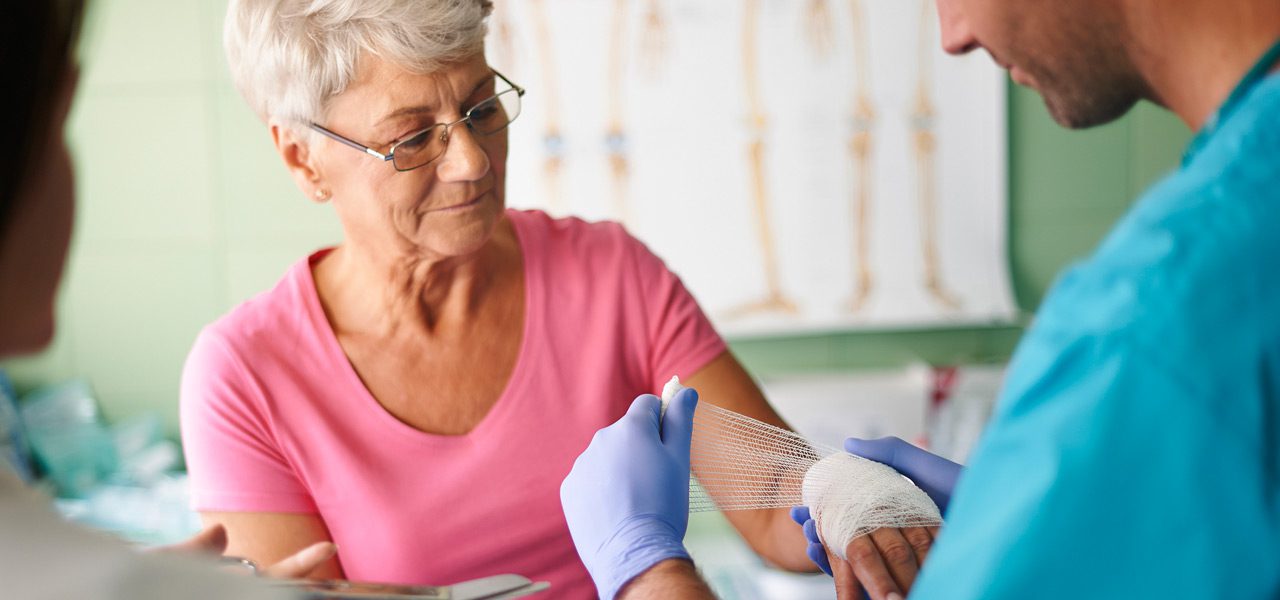

Types And Causes of Wounds
The key characteristics of a wound are tied to how the injury occurred. Below are a few types of injuries and their potential causes.
- Non-penetrating wounds. Typically caused by blunt trauma or friction with other surfaces; the wound doesn’t penetrate the skin, and may include:
- Abrasions involve scraping of the outer skin layer
- Contusions are swollen bruises caused by accumulation of blood and dead cells under the skin
- Concussions are damage to the underlying organs and tissue on head with no significant external wound
- Lacerations are a tear-like wound
- Penetrating wounds. Typically caused by trauma that penetrates the skin, through to the underlying tissue and organs, and may include:
- Stab wounds caused by trauma from sharp objects, such as knives
- Cuts
- Surgical wounds made by intentional cuts in the skin to perform a surgical procedure
- Gunshot wounds caused by firearms
- Thermal wounds. Caused by extreme temperatures, either hot or cold, and can lead to thermal burns, sunburn, and frostbite.
- Chemical wounds. Caused by contact with or inhalation of chemical materials that damage the skin or lungs.
- Bites and stings. Bites caused by humans, dogs, snakes, rodents, scorpions, bats, spiders, and ticks
- Electrical wounds. May cause superficial burn-like or sting-like wounds and more severe internal damage as a result of electrical shock.
Dressing a Wound
The first step in dressing a wound is to assess the bleeding. Our nurses always wear gloves when removing the bandage and assessing the extent of bleeding. Wounds that aren’t bleeding heavily will be cleaned with soap and water. Particles will be removed using tweezers and if necessary, the nurse will apply an antibiotic ointment to support healing. The wound will then be covered with an adhesive bandage.
Types of Wound Dressings
At Active Plus Home Health, Inc., patients may receive the following types of wound dressings:
- Cloth dressing (to protect open wounds)
- Foam dressing (to help maintain a healthy moisture balance)
- Transparent dressing (to easily monitor wounds)
- Hydrocolloid dressing (to speed up healing)
- Hydrogel dressing (to add moisture and speed up recovery)
- Alginate dressing (to protect wounds with excessive drainage)
- Collagen dressing (to treat chronic wounds with a slowed healing time)

