
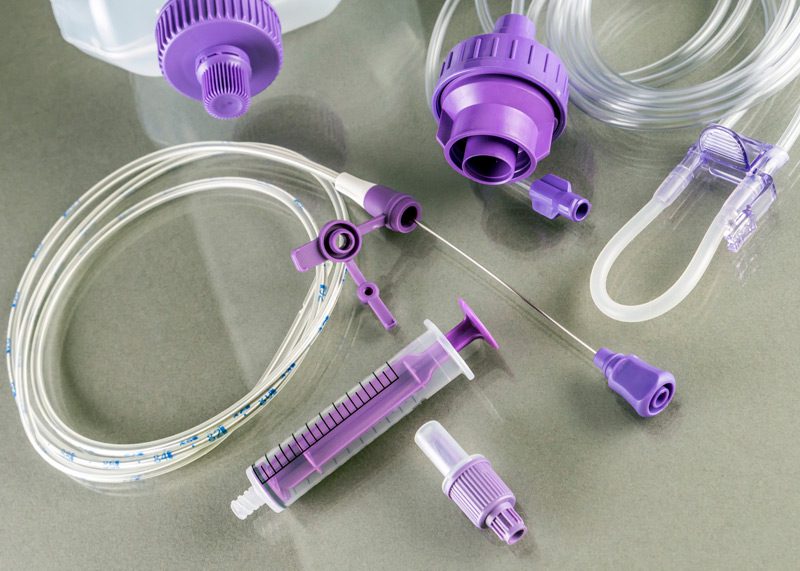
Patients who have undergone a gastrostomy have a tube, or G-tube, placed in their stomach to deliver food and or medicine, as well as to vent the stomach for air or drainage. Proper G-tube management requires a specific list of tools and supplies.
Supplies Necessary For G-Tube Management
A nurse will use the following supplies to care for a G-tube:
- Tape
- Scissors
- Soap and water
- Clean gauze pads
- Extension set
- Syringe and water for flushing
- Securement device
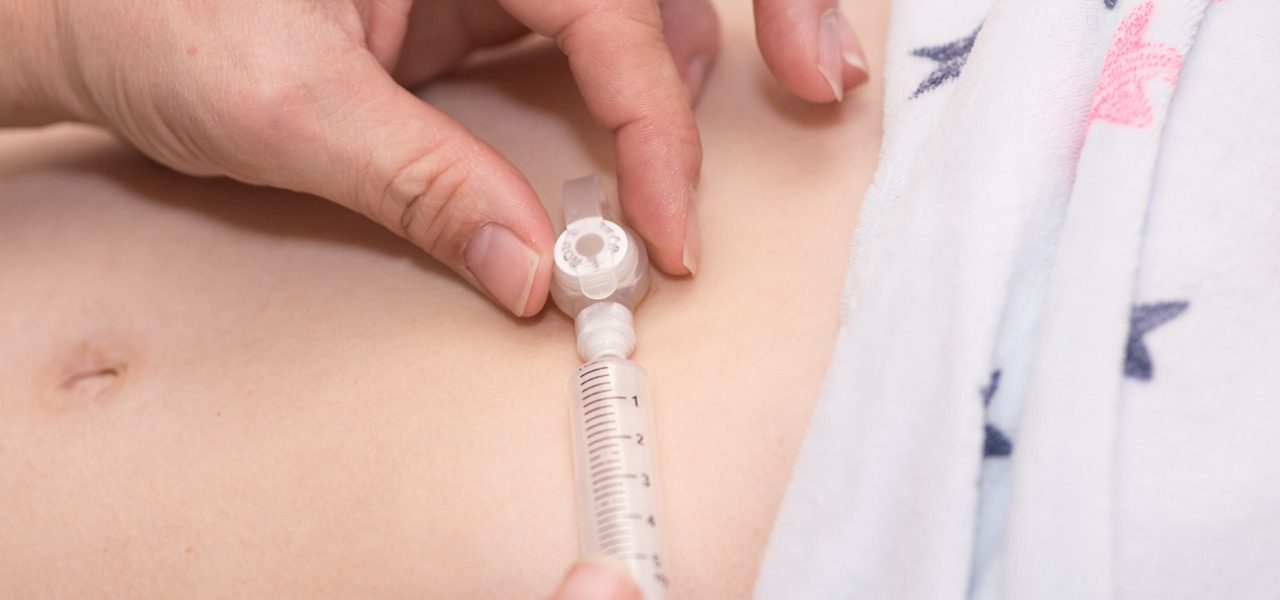
How to Care For The G-Tube Site
A nurse will begin by washing their hands with soap and water. Next, he or she will remove the old dressing and inspect the G-tube site. They’ll look for signs of swelling, redness, drainage, or excess skin growing around the tube. A small amount of clear tan drainage is no cause for concern.
Using soap and warm water, the nurse will wash the skin around the tube and remove any drainage and or crusting. The skin will be patted dry. If necessary, the nurse will apply a dressing around the G-tube, but will avoid lotions and ointments unless directed by a healthcare professional.
Guidelines For Flushing The G-Tube
It’s important to flush the G-tube with water at least once every eight hours. The G-tube should also be flushed before and after any tube feeding and medications. Patients should consult a doctor or nurse to find out the amount of water that should be used to flush the G-tube if they ever need to flush it themselves.
How to Administer Medication And Flush The G-Tube
Liquid medication is poured directly into the medication port. Pills may need to be crushed and mixed with water to create a liquid solution. Capsules may also need to be opened and dissolved with water to create a liquid. Patients should consult with a doctor or pharmacist before taking these steps on their own.
Only one medication is administered at a time, and water is poured after each one. Extension sets should be changed regularly and removed from the G-tube when not in use, feeding, or administering medication.
Warm water is used to clean and rinse the extension sets. Be sure to air dry on a clean surface and throw away sets with residue, damaged plastic, or kinks during feeding.
How to Vent The G-Tube
The venting tube may be used to remove extra air or fluid from the stomach. The patient’s care team will provide instructions for venting the G-tube.
Troubleshooting Problems With The G-Tube
Every now and then, patients may experience issues with their G-tube. Below are a few common problems and solutions.
- The G-tube was pulled out: Place the tube into the opening about one to two inches deep and tape the tube to the stomach. Visit the doctor’s office or emergency room to correctly insert the G-tube as soon as possible. The G-tube must be placed within one to four hours to prevent the tract from closing.
- Redness, irritation, soreness, and foul odor: The cause may be leakage or infection. A nurse may use a barrier cream to address this issue.
- Leakage at the G-tube site: Call a doctor or nurse for advice. More water may need to be added to the balloon port. Or, the patient may need a dressing or protective cream.
- Clogged G-tube: To correct this, a 10 ml syringe may be used to slowly push or pull warm water into the tube. Repeat every 10 to 15 minutes.

